Conservation-smart credit line for agriculture
In a nutshell
The Conservation & Climate-Smart Lending Platform (C2SLP) is based on the inclusion of requirements for improved environmental practice in agricultural loan terms, which makes improved on-farm conservation a contractual obligation and a component of a farmer’s credit score.
Farmers repay their loans with interest, but also build environmental restoration systems on their farmland, thereby creating both financial and environmental returns. The C2SLP is scalable and flexible: it can be adapted to different agro-ecological contexts and land management measures and as a pay-as-you-go model, it is designed to save costs for lenders and investors
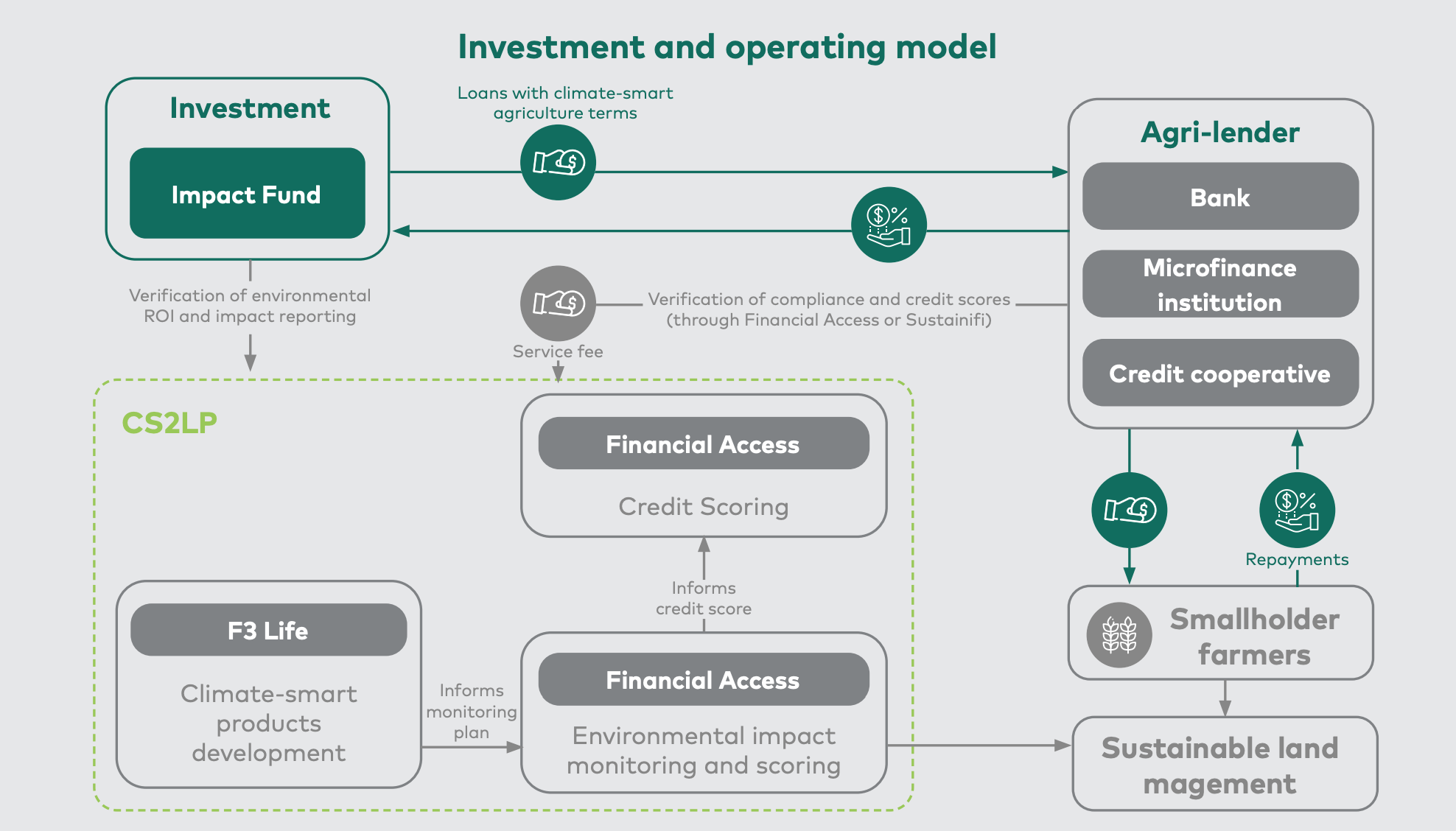
Investment and operating model
Investors seeking defined financial and environmental returns place a debt investment with an agri-lender (such as a bank, microfinance institution, or credit cooperative) who targets credit-worthy smallholder or emerging commercial farmers. Using this debt investment, the agri-lender then issues loans to its smallholder farmer clients. This loan is issued under a conventional loan agreement, but the contract includes terms with requirements for sustainable agricultural practices. Farmers are screened for creditworthiness, either by the lender or using digital scoring tools developed by Financial Access and tailored to the specific context and needs of the lender. This leads to the creation of a portfolio of bankable smallholders, who are then issued conservation and climate-smart loans. Under the terms of their loan, they implement the agricultural practices designed to deliver the conservation or climate benefits targeted by the investors. Evidence of the improvements made by the farmers is collected, pushed to the agri-lender, and can be used to inform credit scores.
Investors will typically invest in agri-lenders at a return of 6–12% per annum on a 3-year term. Loans by agri-lenders to farmers are either seasonal (3-6 months) or annual, depending on the crop and loan type. Interest rates charged by agri-lenders vary according to the financial institution and the country.
Impact measurement
Specific metrics can be designed with the project partners on a case-by-case basis to measure the delivered ecosystem goods and services, such as habitat protection and restoration, water regulation, erosion control, and pollination. Standard metrics, aligned with the leading impact measurement frameworks such as IRIS+ and LandScale, may include social outreach, ecological management area, area of trees planted, and ecosystem services provided. The Sustainifi impact monitoring and reporting platform has been designed specifically for this purpose.
Scalability and replication
The model has been developed for adoption in a variety of contexts and value chains, including coffee, tea, sugar, maize, cocoa, dairy, and cotton, and can easily be adapted to other crops. Conservation and climate-smart credit products can also be adapted at low cost for use in a variety of agro-ecological contexts. There is an estimated USD 170 billion financing gap in the smallholder farmer market globally. Increasing requirements around the disclosure of climate risks by financial institutions and environmental impacts linked to agricultural loans is also expected to drive demand for the types of services provided by the C2SLP.